Although earwax might not look pretty, this oily substance is full of antibacterial and protective properties essential for keeping your inner ear healthy. Usually, the wax comes out of your ears by itself, helped along by the movement of your jaw, but sometimes it can build up and cause discomfort and hearing problems. These blockages can occur for several reasons, including:
- Narrow or hairy ear canals
- Regular exposure to moisture causing the wax to swell
- Age — earwax becomes dryer as we get older
- Wearing earplugs, earbud headphones or hearing aids.
Syringing, also known as ear irrigation, is the method most commonly adopted to remove excessive earwax. However, recently, many people have been converting to microsuction ear wax removal. In this article, we’ll look at the pros and cons of both techniques and advise you on the safest way to keep your ears clean.
Signs of an Earwax Build-up or Blockage
Booking a physical examination from a professional audiologist at a hearing clinic is the best way to determine whether you’ve got an earwax blockage. But, as a good indicator that you might be suffering from a build-up, here are a few warning signs to keep in mind:
- Impaired hearing
- A sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Mild tinnitus (a low or high-pitch ringing in one or both ears)
- Dizziness, balance problems and vertigo
- Persistent earache
- Itchiness and irritation in the ear canal, and possibly a discharge or strange odour
- Constant, unexplained coughing.
Luckily, all of these problems are temporary and can quickly be fixed with specialist ear wax removal treatment, immediately improving your overall quality of life.
The Differences between Syringing and Microsuction
At Regain Hearing, we offer two types of ear wax removal services — syringing and microsuction. While both methods safely remove blockages and improve inner-ear health, there are certain risks associated with syringing.
Ear syringing takes between 15 to 30 minutes, shooting a low-pressure stream of warm water into the ear to dislodge the wax and clear the canal. While this procedure shouldn’t be painful, some patients feel uncomfortable when the water touches their eardrums. Also, it can be quite messy with both the water and sticky wax draining from your ear. In addition, audiologists can’t carry out this procedure on those who’ve recently had ear surgery or are suffering from catarrh, a perforated eardrum or ear infection.
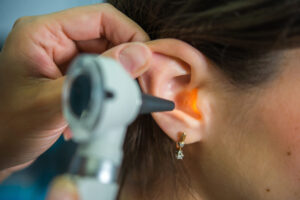
Microsuction ear wax removal is our preferred method. It works by gently suctioning the wax from the ear, similar to a vacuum cleaner. As the audiologist uses a microscope to view the inner ear as they remove the blockage, it’s much more precise and entirely without risk. The whole process only lasts between 10 and 20 minutes, and there’s less risk of infection, too, seeming as the process is done dry and there is no direct contact with the skin of the ear canal.
What’s the Safest Way to Remove an Earwax Blockage?
Although both methods of earwax removal are equally effective, microsuction carries the lowest risk overall. However, you should always ask a trained professional to remove blockages from your ears — never do it yourself at home. Pushing cotton buds, fingers, hairpins, needles, or anything else into your ear not only moves the build-up further down the canal but can also cause significant damage to your eardrum.
Think you might be suffering from an earwax blockage but aren’t sure what the best method is to remove it? Contact Regain Hearing’s highly qualified team of audiologists and book a consultation today to discuss possible treatments. Book ear wax removal in Maidstone, Eltham and London, we’re passionate about helping our patients regain an excellent quality of hearing.
